- Afghanistan
- Africa
- Budget Management
- Defense
- Economy
- Education
- Energy
- Environment
- Global Diplomacy
- Health Care
- Homeland Security
- Immigration
- International Trade
- Iraq
- Judicial Nominations
- Middle East
- National Security
- Veterans
- President's Cabinet
- USA Freedom Corps
- Faith-Based & Community Initiatives
- Office of Management and Budget
- National Security Council
- USA.gov
- Introduction
- Military Commitments
- Law-Enforcement Actions
- Legislation and Diplomatic Actions
- Financial Actions
- Assistance to Afghanistan
- Protecting the Future
1. Introduction
Following the appalling events of September 11th, countries across the world expressed their support for action against terrorism. That support now forms the foundation of a remarkable world-wide coalition.
The Coalition rapidly established its objectives. The first things to do were: to stop Usama Bin Laden and the Al Qa’ida network and to ensure that Afghanistan ceased to harbour and sustain international terrorism.
The Coalition’s objectives remain:
- to do everything possible to eliminate the threat posed by international terrorism;
- to deter states from supporting, harbouring or acting complicity with international terrorist groups.
We have destroyed a number of Al Qa’ida training camps in Afghanistan and removed the corrupt Taliban regime. The international community is fully committed to helping Afghanistan recover from the destruction wrought by the Taleban and its close ally - Al Qa’ida.
While Coalition action has achieved a great deal in shutting down terrorist training camps, the Coalition’s campaign in Afghanistan and against terrorism continues.
|
|
"What we have found in Afghanistan confirms that, far from ending there, our war against terror is only beginning…If we stop now – leaving terror camps intact and terror states unchecked – our sense of security would be false and temporary." President G.W. Bush, 29 Jan 2002 |
The threat to nations and people across the world still continues…..
|
|
"What we now have to face is the fact that there are irresponsible states who either have, or are actively seeking, biological, chemical and nuclear weapons. This is the threat which President Bush rightly highlighted in his State of the Union Speech. And if we continue to allow these states to obtain and develop these weapons, we may find out too late their potential for destruction. " Prime Minister, Tony Blair 6 March 02 |

|
|
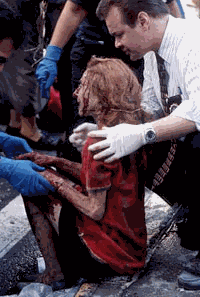
| Citizens of dozens of countries died in the attacks on New York, Washington and Pennsylvania |
|
|
Countries across the world have responded with military action, changes to security measures to freeze terrorist finances, help with the investigation, new laws to prevent and prosecute terrorism, and humanitarian aid to Afghanistan |
|
This report lists some of the actions taken by the Coalition The report can not list all the measures taken, but goes some way to show how countries of the world are uniting to defeat international terrorism |
2. Military Commitments
|
A critical element to the war on terrorism remains the building and sustaining of a strong coalition of nations dedicated to freedom and security. Coalition forces make important contributions to the War on Terrorism across the spectrum of operations. Particular contributions include, but are not limited to, providing personnel, equipment and assets for use on the ground, air and sea. Coalition members have also provided liaison teams, participated in planning, provided bases and have granted over-flight permissions. And some are now working to train the new Afghan security force. To date, 17 nations have deployed to the US Central Command’s area of responsibility with over 16,500 troops. This coalition is working hard everyday to defeat terrorism, wherever it may exist. |
Below is a breakdown of support from some of our coalition partners.
The Americas
USA
The U.S. has taken direct military action in Afghanistan, plus co-operated militarily with many governments across the world.
|
|
"So long as training camps operate, so long as nations harbor terrorists, freedom is at risk. And America and our allies must not, and will not, allow it." President G.W. Bush 29 Jan 2002 |
Canada
- Canadian representatives arrived at US Central Command (CENTCOM) on 01 Oct 01. Currently there are 61 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Canada currently has 2,259 personnel in the CENTCOM AOR (747 land, 447 air and 1065 naval personnel).
- The Canadian Naval Forces have been engaged in Maritime Interdiction Operations (MIO), Leadership Interdiction Operations (LIO), escort duties and general maritime surveillance between the North Arabian Gulf and the North Arabian Sea.
- Canadian Air Force CC 150 Polaris (Airbus) and 3 CC130 (Hercules) aircraft have conducted strategic and tactical airlift. They have moved over 4.3 million pounds of freight to date. 2 CP 140 Aurora (P3C) aircraft are employed in MIO/LIO operations as part of CTF 57. 44 missions and 391 flight hours have been logged to date. Organic helicopter assets have flown in excess of 700 missions.
- Canada’s Light Infantry Battle Group has deployed as part of TF Rakkasam with 693 personnel and 12 COYOTE armoured reconnaissance vehicles. These forces have been deployed to Qandahar for security and combat operations. A third Infantry Company will soon be added.
- Special Operations Forces are currently in Afghanistan performing the full spectrum of missions.
- Canada contributed the first coalition Task Group to arrive in CENTCOM AOR. Recently, HMCS TORONTO operating in the North Arabian Sea intercepted a small vessel laden with 4,500 pounds of hashish (valued at over $60 million). The vessel was abandoned by its crew during the interception. The cargo and vessel were subsequently destroyed.
European Nations
UK
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM 18 Sep 01. There are currently 43 personnel at CENTCOM.
- RADM Burnell-Nugent serves as Deputy Commander for all coalition naval forces in theatre, responsible for co-ordinating extensive operations
- British ground forces have participated in both Operation Enduring Freedom/Operation Veritas and ISAF missions (Operation Fingal). "B" Company of 40 Commandos and Royal Marines deployed to Kabul and has contributed to mine clearing operations, including the provision of specialist equipment at both Bagram and Kabul International airports.
- The UK was the first nation to send military representatives and campaign planners to CENTCOM.
- They have deployed the largest Naval Task Force since the Falklands War to support OEF. Additionally, they have provided the only coalition Tomahawk Land Attack Missile platforms to launch missiles during the commencement of OEF hostilities.
- The UK has been involved from the outset alongside US forces. It has fired Tomahawk missile salvos and flown sorties in support of US strike aircraft. It has also made available to the United States the base at Diego Garcia.
- The UK has assigned an Amphibious Task Group to OP VERITAS, currently led by the Royal Navy’s Landing Platform Helicopter (LPH), HMS OCEAN. Other ships involved are:
- The destroyer HMS YORK;
- The frigates HMS CAMPBELTOWN and HMS PORTLAND;
- A Tomahawk missile armed submarine presence;
- Six ships of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary, the RFAs BAYLEAF, DILIGENCE, FORT GEORGE, FORT ROSALIE, SIR PERCIVALE and SIR TRISTRAM.
- The Survey Ship HMS SCOTT is also in the area.
- Since 21 December 2001 the Royal Navy has taken part in coalition maritime interdiction operations to seize personnel or equipment, provided that compelling intelligence is obtained linking the target to Al Qa’ida or the Taliban.
- The RAF currently has six reconnaissance and refuelling aircraft assigned to OP VERITAS, consisting of Boeing E3D Sentry AWACS, Nimrod MR2 maritime patrol aircraft and TriStar tankers.
- A number of C130 Hercules aircraft have been deployed, although these are primarily used to support the ISAF.
- We also have a number of helicopters with the Amphibious Task Group, supporting our activities in and around Afghanistan.
- In all, excluding ISAF troops, there are about 3,600 UK personnel in the region.
UK’s INVOLVEMENT IN OPERATION FINGAL (ISAF)
- The UK agreed to act as Lead Nation of the ISAF for the first three months of its deployment. Major General John McColl has been appointed Commander of the ISAF during this period.

A few hours before addressing the US Congress and the world, President Bush talks privately with British Prime Minister Tony Blair in the Blue Room at the White House Sept. 20.
France
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 08 Oct 01. There are currently 15 personnel at CENTCOM.
- The French Air Force deploying C-160 and C-130 aircraft to Dushanbe, Tajikistan, have provided Humanitarian Assistance as well as national and coalition airlift support. Two KC-135 aircraft will deploy to Manas, Kyrgyzstan to provide aerial refuelling. Six Mirage 2000 fighter aircraft will also deploy to Manas. Atlantique aircraft are deployed to Djibouti under national control.
- French engineers helped construct runways, a Tent City and a munitions storage facility at Manas. France also provided airfield security (with dogs), a Field Mess Unit, a Deployable Weather Bureau, and a CMO Team. Additionally, France deployed and Infantry Company to Mazar-e-Sharif, Afghanistan to provide area security.
- One French officer is currently serving as an air co-ordinator at the Regional Air Movement Control Centre (RAMCC).
- France is providing their only Carrier Battle Group to support combat operations in the North Arabian Sea. Aircraft from this Battle Group have flown over 1,500 hours for OEF to date. France’s naval contribution to OEF accounts for approximately 24 percent of their entire naval forces.
- Additionally, France has been the only non-US country taking part in the operational build-up at Manas airfield in Kyrgyzstan.
Belgium
- Belgium representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 19 Oct 01. Currently there are 4 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Belgium is providing one officer to the Coalition Intelligence Centre (CIC) at CENTCOM and one officer to the Regional Air Movement Control Centre (RAMCC) to serve as Deputy Chief of Operations.
- Belgium Air Force C-130 aircraft delivered a high protein food supplement (UNIMIX) from Denmark to Dushanbe, Tajikistan.
- Their A-310 (Airbus) delivered 250,000 vaccinations for children under the United Nations Children’s fund (UNICEF) program.
- Belgium led the largest multinational Humanitarian Assistance (HA) mission, which included Belgium, Spain, Netherlands and Norway. This mission provided 90 metric tons of UNIMIX to feed starving children in Afghanistan and set the standard for follow-on HA operations.
Germany
- Operation Enduring Freedom - up to 3,900 troops
- A Nuclear Biological and Chemical unit equipped with "Fuchs" armoured reconnaissance vehicles for detecting nuclear, biological and chemical contamination.
|
|
"On 7 October the United States, supported by Great Britain, launched the military operation known as Enduring Freedom. The US Administration has now approached us with a specific request. It covers the provision of ABC defence forces, a unit to evacuate the wounded, special forces of the Bundeswehr, air transport facilities as well as naval forces- for instance to keep shipping lanes open and to protect vessels with hazardous cargoes. The Federal Cabinet decided yesterday to comply with this request" Chancellor Gerhard Schröder in the German Bundestag, 8 November 2001 |
- The unit and crew of 250 are currently deployed to Kuwait for a defence exercise and will be on standby afterward in Germany.
- "Flying Hospital" - medical evacuation Airbus A310 and crew.
- A Special forces naval task force is taking part in CENTCOM’s operations around the Horn of Africa, helping to disrupt the communication routes of terrorist organisations and countering piracy.
- The core of the task force are three frigates and five fast patrol boats. Naval aircraft are also conducting fact-finding missions over Kenya.
- On operation Noble Eagle, German troops are part of the crews of NATO AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System) that have been patrolling US airspace since October 2001.
- ISAF - More than 700 soldiers, with a total of 1,200 available, are leading the 1,450-strong contingent supported by The Netherlands, Austria and Denmark deployed in Kabul.
Denmark
- Denmark's representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 02 Nov 01. There are currently 5 personnel at CENTCOM.
- The Danish Air Force is providing 1 C-130 aircraft with 75 crew and support personnel. These assets began deploying on 20 Feb 02. As of 21 Feb 02, 30 Danish personnel have arrived in the AOR. Additionally, Denmark is scheduled to provide 4 F-16 aircraft in an Air to Ground role with pilots and support personnel. Support availability at host base will determine timeline for force deployment. These assets are on standby in Denmark.
- Approximately 100 Special Operation Forces personnel have deployed to the AOR as part of a multinational unit under US command.
- Denmark will soon become one of the first coalition countries to operate an airlift aircraft from the newly formed Logistical "Hub" that has recently become operational at Manas airbase.
Czech Republic
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 09 Nov 01. Currently there are 3 personnel at CENTCOM.
- 251 personnel are deploying to Camp Doha, Kuwait to perform local training as well as AOR-wide Consequence Management (CM) support
Finland
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 22 Jan 02. There are currently 3 personnel at CENTCOM.
- The Finnish Military Liaison team at CENTCOM continues to concentrate on Civil Military Operations (CMO), with an objective to facilitate co-operation and co-ordination between ISAF, OEF and UN operations in Afghanistan.
- Finland is currently assisting Humanitarian Assistance organisations in Afghanistan in an effort to promote the long-term reconstruction of the country.
- Finland is providing the largest coalition Civil Military Operations (CMO) unit in Kabul in support of ISAF. This unit currently consists of 50 officers.
Greece
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM 19 Dec 01. There are currently 3 personnel at CENTCOM.
- The Greek's have offered one Frigate which will be deployed into the CENTCOM AOR on 15 Mar 02.
- Greece has committed to provide 1 engineering company and 1 C-130 aircraft for tactical airlift in support of ISAF Operations.
Italy
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM 8 Oct 01. There are currently 13 personnel at CENTCOM.
- The Italian Air Force is scheduled to deploy 1 C-130 to Manas airfield following initial force rotation.
- Italian personnel have been committed to both OEF and ISAF operations.
- Italy has provided their only Carrier Battle Group to support combat operations in the North Arabian Sea. They have deployed over 13 percent of their entire naval forces for use in OEF.
Norway
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 15 Nov 01. There are currently 6 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Norwegian Hydrema 910 mine clearing vehicles and personnel have been responsible for clearing over 180,000 square meters of terrain on Qandahar airfield and its surroundings.
|
|
"I'm proud to say a certain number of Norwegian special forces are in place in Afghanistan to support the Americans in the military operation 'Enduring Freedom," Kristin Krohn, Norwegian Defence Minister, 07 Jan 2002 |
- SOF forces are currently providing the full spectrum of SOF missions and were deployed by national means. Air Force C-130 aircraft are providing tactical airlift support and re-supply for these SOF forces. C-130 aircraft have also conducted numerous HA missions and are soon scheduled to deploy to Manas.
- Norway is scheduled to deploy fighters to Manas following the initial force rotation.
- Norway’s SOF exploitation missions have yielded valuable Human Intelligence (HUMINT). Additionally, Norway has provided 15 hardened vehicles ($1.5 million) that are currently supporting SOF missions and providing leadership transport.
Poland
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 19 Nov 01. There are currently 5 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Poland is currently planning the deployment of combat engineers and logistics platoons to Bagram. Poland has also planned for 20 soldiers to deploy to Kuwait to support MIO operations in the CENTCOM AOR.
Portugal
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 13 Dec 01. There are currently 2 personnel at CENTCOM.
Netherlands
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 21 Oct 01. There are currently 7 personnel at CENTCOM.
- An Air Force KDC-10 is currently deployed to Incirlik and conducting Strategic airlift for ISAF. This aircraft will then re-deploy to Al Udeid, Qatar. To date, C-130 aircraft have completed 3 HA flights under national flag. The Netherlands will soon deploy 1 C-130 aircraft to Manas and are scheduled to deploy following the initial force rotation.
- Two Dutch naval frigates are currently operating in the CENTCOM AOR. Other naval ships along with Air Force P-3s will relieve U.S. units in SOUTHCOM AOR.
- One person is scheduled to work as a planning officer at the Regional Air Movement Control Center (RAMCC).
- RNLNS Van Almonde assisted a U.S. E-2 and S-3 aircraft in a Search and Rescue (SAR) mission to find a Pakistani Mirage that was thought to have gone down 23 nautical miles off the coast of Pakistan.
Romania
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 15 Nov 01. There are currently 2 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Romania is currently in the process of approving basing and over-flight permission for all U.S. and coalition partners.
- Romania is currently in the process of planning and co-ordinating the use of infantry units, mine clearing equipment and engineers to support ongoing requirements for OEF.
Russia
- Country representative arrived at CENTCOM on 30 Nov 01.
- Russia has supported HA operations by transporting over 420,296 tons of food commodities, 2,198 tons of medicines, 15,282 beds, 1,200 heaters, 13 mini electric power stations, 780 tents, 11,000 blankets, 49,674 bedding kits, 11,000 pieces of kitchen utensils, and 9 tons of detergents.
- Russia provided the first coalition hospital in Kabul on 29 Nov 01. The hospital treated 5,235 patients before Russia turned the facility over to the local population on 25 Jan 02.
Spain
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 05 Nov 01. There are currently 9 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Spain will soon deploy 1 P-3B to Djibouti, 3 C-130s to Manas and 2 naval frigates to the CENTCOM AOR to support continued operations in OEF.
- Spain provided a hospital in Bagram on 8 Feb 02. As of 20 Feb 02, this hospital has treated 607 patients and has expanded its operation to conduct over 2 hours of humanitarian aid calls per day.
|
|
"The new terrorism that acted against the United States, reminds me of the experience lived by Spain in the last few years, and to reiterate my firm convictions which are receiving more and more world-wide recognition: All terrorism is the same, there is neither better nor worse, nor good or bad, they are all abominable. Therefore, there are no distinctions to be made, simply all of them are terrorists." Federico Trillo, Spanish Defence Minister, at the 38th Conference on Security Policy, 2 Feb 2002 |
Sweden
- An intelligence unit, tied to the UK Headquarters of ISAF, totalling 45 people
- Two C-130 transport aircraft in support of ISAF
- Logistics support for humanitarian aid distribution provided by the Swedish Rescue Services Agency, some 20 professionals.
Asia-Pacific
Australia
- Australian representatives arrived at U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM) on 27 Sep 01. Currently there are 7 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Australian Special Operations Forces (SOF) are currently in Afghanistan performing the full spectrum of SOF missions.
- Australian Air Force C-130s transported national forces to the Area of Responsibility (AOR), and while there, they supported Director of Mobility Forward (DIRMOBFOR) tactical lift requirements.
- Fighter aircraft were also deployed to perform Combat Air Patrol (CAP) missions at Diego Garcia. Soon Australia will deploy 2 KC-135 aircraft to Manas, Kyrgyzstan. Australian Air Force will fill a key wing leadership position at Manas (Operations Group Commander).
- Australia has numerous ships deployed to the AOR supporting Combined Forces Maritime Component Commander (CFMCC) operations.
- The National Command Element is forward deployed in Kuwait providing command and control for deployed forces.
- Australia suffered the first non-U.S. fatality: on February 16, 2002 Sgt. Andrew Russel was killed in action as the result of a land mine explosion..
Philippines
- The government of the Philippines has pledged the use of facilities on Philippine soil for the anti-terrorist coalition. It is forging a regional grouping to fight terrorism with Malaysia, Indonesia and Thailand.
|
|
"Destroying terrorism is the immediate and overriding objective" Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo, President of the Philippines, 26 September, 2001 |
New Zealand
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 8 Oct 01. There are currently 6 personnel at CENTCOM.
- New Zealand provided logistic and HA airlift support in Afghanistan with Air Force C-130 aircraft. These aircraft were made available to help move the backlog of equipment and supplies needed for OEF.
- Their 7-person Air Loading Team (ALT) was deployed to support ISAF.
- New Zealand will soon deploy 8 officers to staff the ISAF headquarters.
- As part of a combined operation, New Zealand SOF units recovered valuable equipment and forwarded it for exploitation.
Middle East
Egypt
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 28 Nov 01. There are currently 3 personnel at CENTCOM.
Jordan
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM 07 Oct 01. There are currently 2 personnel at CENTCOM.
- An "Aardvark" mine clearing unit and personnel are currently deployed to Qandahar.
- One person is scheduled to work as a planning officer at the Regional Air Movement Control Centre (RAMCC).
- Jordan has provided basing and over-flight permission for all U.S. and coalition forces.
- Jordan’s deployment of Level II Field Hospital and Airborne Infantry Company to Mazar-e-Sharif has enabled the treatment of over 17,000 patients (including over 8,000 women and children) and performed over 150 surgical operations.
Bahrain
- No country representatives are currently present at CENTCOM; however, there is one Naval Liaison Officer (LNO) at U.S. Naval Forces Central Command (NAVCENT).
- Bahrain maintains fighter units on continuous strip alert providing defensive CAP that protect national and coalition forces in Bahrain.
- One Frigate and associated personnel are supporting OEF naval mission in the AOR.
- Basing and over-flight permissions have been significant enablers for Coalition Forces.
|
|
"We have supported and participated in the international campaign against terrorism and the efforts to eradicate its elements, shelters and sources of finance. We have done so on the basis of our firm principles against terrorism, and indeed all acts of violence and extremism, which contradict the teachings of Islam and the civilised standards of humanity that we believe and support." Bahrain Foreign Minister Shaikh Mohammed bin Mubarak Al Khalifa, 28 Feb 2002 |
Qatar
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 6 Dec 01. There are currently 3 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Qatar maintains fighter units on continuous strip alert providing defensive CAP protection for national and coalition forces in Qatar.
- Qatar led the way in the early stages of OEF by granting over-flight and basing clearance for U.S. and coalition forces.
United Arab Emirates
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 01 Nov 01. There are currently 3 personnel at CENTCOM.
- The United Arab Emirates have provided basing and over-flight permission for all U.S. and coalition forces.
- Air Force C-130 aircraft have supported HA operations by airlifting supplies into Central Asia. They have conducted 3 flights to date.
Asia
Turkey
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 11 Oct 01. There are currently 3 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Turkey has provided basing and over-flight permission for all U.S. and coalition forces.
- One Turkish officer is scheduled to work as a planning officer at the Regional Air Movement Control Centre (RAMCC).
- Turkey was the first coalition country to provide critical KC-135 aerial refuelling support for U.S. aircraft during their transits to the CENTCOM AOR.
|
A mechanical digger gets to work on |
"Terrorism is a crime against humanity. We strongly condemn all the perpetrators of such crimes and the recent heinous terrorist attacks against the USA. All nations should unite their will and co-ordinate their acts in the fight against terrorism. Turkey, as several other European countries, has suffered from terrorism. We must all stand up together to eradicate this scourge." Ismail Cem, Turkish Foreign Minister to the European Conference, Brussels, 20 Oct 2001 |
Pakistan
- Pakistan supports the military intervention in Afghanistan, offering information, over-flight rights and logistic support, and intervening to stop fleeing Taliban and Al Qa’ida fighters trying to reach safety.
Republic of Korea
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 16 Nov 01. There are currently 5 personnel at CENTCOM.
- A Republic of Korea naval vessel transported over 500 tons of critical construction material from Singapore to Diego Garcia to support the demand for OEF building materials. Additionally, they have pledged over 45 million dollars to aid in the reconstruction of Afghanistan.
- Republic of Korea will soon deploy a Level II hospital to Manas and has already sent 2 liaison officers to begin co-ordination efforts.
- South Korean Air Force C-130s have flown 11 flights between Seoul, Korea and Diego Garcia as well as 5 flights to Islamabad. These flights were responsible for transporting over 45 tons of humanitarian relief supplies valued at $12 million.
Uzbekistan
- Country representatives arrived at CENTCOM on 26 Dec 01. There are currently 5 personnel at CENTCOM.
- Uzbekistan has helped relieve Strategic airlift requirements by leasing IL-76 transport aircraft to coalition members to move forces and equipment into the CENTCOM AOR.
Cambodia
- Cambodia has offered the coalition the use of their airports and ports if needed.
|
|
"The world must make every effort and action to combat terrorism" Nordom Sihanouk, King of Cambodia in a statement to President Bush, 12 September 2001 |
|
The War on Terrorism is a broad-based effort that will take time. Every nation has different circumstances and will participate in different ways. This mission and future missions will require a coalition that is ready to take on the challenges and risks associated with such a operation. The accomplishments to date can be directly attributed to a focused and unwavering coalition. |
3. Law-Enforcement Actions
|
All over the world countries are taking law enforcement action against the Al Qa’ida network. Most of these actions concern information sharing and co-operation over borders. There are many examples of direct actions against individuals and organisations linked with Al Qa’ida. |
The very nature of these investigations means we are not able to divulge as much information about them as we would like, but below are just a few that we can discuss:
|
Spain In 2001, Spain conducted a number of major operations against Islamic terrorist networks, as follows:
Spain is also actively collaborating with Europol in regard to the supply and exchange of information on terrorist groups. |
|
France Ahmed Laidouini, a Frenchman of Algerian descent, was arrested on December 24th. He is suspected of training in Al-Qa’ida camp in Afghanistan in 1998 and becoming a liaison between Al Qa’ida cells |
|
Germany The Public Prosecutor General has initiated 17 investigative proceedings related to the attacks or to the phenomenon of Islamic-fundamentalist terrorism. The investigations have led to arrest warrants and international searches for Said Bahaji, Ramzi Omar (alias Binalshib), and Zakaria Essabar, who fled Germany shortly after the attacks. A fourth suspect has been apprehended and is in custody pending interrogation. The traditionally close and trusting co-operation between German and US authorities, particularly the FBI and CIA, has intensified since September 11. Up to 15 liaison officers from US authorities are participating in the investigation in Germany. The Federal Criminal Police Office has two permanent liaison officers in Washington and has sent two officers from the special commission to the FBI. |
|
UK The Metropolitan Police Service (MPS) is giving the FBI every support and assistance. The terrorist attack of September 11 has led to the largest terrorist investigation by the MPS outside the UK. A total of move than 5000 actions have been generated Teams of family liaison officers were sent to New York to assist families of British victims of Sept 11. The casualty bureau at New Scotland Yard received over 26,000 calls. Yasser Al-Siri has been charged with conspiracy to murder in connection with the assassination of General Masoud. Sulayman Balal Zainulabidin has been charged under the Terrorism Act 2000 in connection with the provision of paramilitary training. Sheik Abdullah el-Faisal has been charged with encouraging others to murder. |
|
Italy In February 2002 Italian investigators discovered evidence pointing to a bomb plot against the US embassy in Rome. Holes were found carved into an underground passageway next to the mission, which police believe could have been used to plant a bomb by militants linked to Osama bin Laden's al-Qa’ida network. Photos of the holes - large enough for a person to get through - have been forwarded to prosecutors handling the case of Moroccan men arrested with suspected bomb-making equipment. The Moroccans were found with large quantities of a cyanide compound, explosive powder and maps of the water network around the US embassy on Via Veneto in the heart of Rome. After the arrests, police and maintenance staff checked tunnels around the embassy complex that carry water, gas and electricity to buildings in the area, and found a hole cut into a wall next to the diplomatic mission. |
|
Malaysia The Government of Malaysia announced on January 4th that it had arrested members of an Islamic militant group with links to Zacarias Moussaoui, the accused 11 September terrorist attack conspirator. The suspects all belonged to a group the authorities call Kumpulan Militan Malaysia (KMM), had connections with Moussaoui when he was in Malaysia in September and again in October 2000. |
|
Kenya The bombing of the US Embassy in Nairobi in August 1998 by al-Qa’ida, in which more than 200 Kenyans were killed, is still vivid in the memories of the Kenyans. Kenya has extradited to the US all the suspects arrested in Kenya in relation to the 1998 bombing. It is a member of Interpol and has contributed repeatedly by extraditing international signalled criminals. |
|
Countries have reviewed and, where needed, tightened up their laws against international terrorism – an important aspect of the campaign |
The Americas
USA
- President Bush called immediately for a world-wide campaign against terrorism.
- He synchronised the application of diplomatic, military, economic, intelligence , and law-enforcement power on a global scale, forming an unprecedented network of nations working to defeat terrorism.
- All nations of the world except one (Afghanistan under the Taliban) condemned the attack and responded positively to the President Bush’s call:
- NATO invoked Article V of the NATO Charter, first time in its history.
- 16 NATO members have contributed troops and military equipment.
- 197 countries and jurisdictions expressed support for the campaign and its objectives.
- 89 countries have granted over-flight authority (28 have granted blanket authority), 76 have granted landing rights, 23 have granted bed-down and basing authority.
- 23 countries have agreed to host U.S. forces involved in offensive operations
- 136 countries have offered some kind of military assistance.
- 142 countries have issued orders freezing the assets of suspected terrorists and terrorist organisations; 190 countries have expressed willingness to do so.
- NATO and ANZUS allies quickly invoked their treaty obligations to support the United States.
- The United States has received 46 multilateral declarations of support. The U.N. General Assembly and Security Council condemned the attacks on September 12.
- NATO allies are assisting directly in the defence of American territory.
Canada
- The Government of Canada has introduced key pieces of legislation. The Anti-Terrorism Act, introduced on October 15, includes measures designed to: identify, prosecute, convict and punish terrorists; provide new investigative tools to law enforcement and national security agencies; and ensure that Canadian values of respect and fairness are preserved through stronger laws against hate crimes and propaganda.
- Canada has ratified 10 of the 12 counter-terrorism conventions of the United Nations. The new Anti-Terrorism Act will allow Canada to ratify the remaining two.
- The Public Safety Act, introduced on November 22, will amend some 18 federal laws to further strengthened the Government’s ability to protect Canadians, prevent terrorist attacks and respond swiftly if a significant threat should arise.
- In addition, amendments to the Aeronautics Act will maximise the effectiveness of the aviation security system and ensure that Canada continues to have one of the safest aviation systems in the world.
Colombia
- Since September 11 it has taken action against suspected financiers of terrorism.
- It now has further proposals for new anti-terrorism bill now in Congress.
Europe
UK
- Even before September 11 the UK had a wide range of legislative measures in place to counteract terrorist activity.
- The centrepiece of this legislative framework was the United Kingdom Terrorism Act 2000. Other relevant legislation included the Immigration Act 1971, the Customs and Excise Management Act 1979, the Extradition Act 1989 and the Export of Goods (Control) Order 1994.
- Following the events of September 11 it was decided to enhance the UK’s existing Anti-Terrorism legislation. This resulted in the Anti-Terrorism, Crime and Security Act 2001which received royal assent on 14 December 2001.
The Netherlands
- Within the country an overall action plan has been put in place and agreements have been reached between the countries on:
- the strengthening of legislation to combat terrorism;
- strengthening of co-operation between the police- and the justice departments of the countries;
- the creation of an adequate infrastructure for the information position of the national security departments; and,
- the strengthening of control mechanisms for the financial sector
Germany
- Chancellor Gerhard Schröder announced on October 11 a second anti-terrorism package that is intended to give security and criminal investigation agencies more efficient means of obtaining information for the purpose of fighting terrorism and crime.
- Germany is continuing its investigation related to the September 11 attacks and has adopted two comprehensive anti-terror legislative packages to strengthen security, disrupt terrorist funding sources, and to improve the tools available to authorities to combat terrorism.
- More than 500 officers of the Federal Criminal Police Force are assigned to a special commission investigating the September 11 attacks.
- Germany hosted the Bonn conference that established the Interim Authority in Afghanistan.
- The German cabinet adopted two comprehensive anti-terrorism packages in September and December 2001, including approximately $1.3 billion (more than 1.5 billion EUR) in funding.
- The measures include provisions for increased air-traffic security and tightening of the act governing private associations to increase authorities and options for acting against extremist associations.
- A change in the criminal code allows the prosecution in Germany of terrorist activities in foreign countries.
- More authority has been granted to the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution, the Military Counter-intelligence Service, the Federal Intelligence Service, the Federal Criminal Police Office and the Federal Border Police, specifically in the gathering and evaluation of information.
France
- In December, President Chirac called upon world leaders to use their financial, legal and intelligence tools to fight international terrorism.
Russia
- Russia has signed the twelve UN Conventions against Terrorism. It hopes to join the Indian project to draw up a general convention against terrorism
Finland
- Finland offered all possible assistance to the US in the aftermath of the September the 11th attacks.
- Finland has agreed with and enforced all the measures taken by the EU to combat terrorism.
- Finland is in the process of ratifying the two UN conventions on terrorism which it has not yet done.
Croatia
- President Mesic has spoken of the role of small countries in the fight against terrorism. In a speech on this role he set out 16 specific proposals including intelligence sharing, suspect extradition and humanitarian assistance.
Greece
- Foreign Minister Papandreou offered to strengthen the Coalition through Greece’s relations in the Mid-East and has travelled extensively to the region.
Asia
Japan
- On 27 September 2001, both Houses of the Japanese Parliament (the Diet) passed a resolution calling on the Government to co-operate fully with the coalition.
- The Anti-Terrorism Special Measures Act and two related Acts were passed by the Diet on 29 October 2001.
|
|
"The terrorist attacks of September 11th changed the world. Such unforgivable acts challenge the dignity of humanity as a whole. The people of Afghanistan are also victims of the Taliban and al-Qa’ida" Opening Statement by Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi at the International Conference on Reconstruction Assistance to Afghanistan, 21 January 2002 |
Singapore
- Usama bin Laden and his network have been outlawed in Singapore.
- The Parliament rushed through new legislation prior to the elections , which gave the Minister for Law the power to implement the provisions of UNSCR 1373.
Indonesia
- Indonesia has stated its commitment to work towards domestic legislation in place to criminalise the provision or collection of funds for terrorism and to freeze terrorist funds or assets.
|
President Bush and Indonesian President Megawati Sukarnoputri , White House Sept. 19. |
- The Indonesian government has also taken steps to enhance aviation security.
- The Government of Indonesia has signed a Memorandum of Understanding. on Combating International Terrorism (MOUCIT).
- MOUCIT covers intelligence exchange, law enforcement co-operation, training, exchanges visits and capacity building.
Malaysia
- Prime Minister Mahathir said that his government would hunt down all militants and extremists until they are no longer a threat to national security.
The Middle East
Saudi Arabia
- The authorities have pledged their full co-operation to fight against terrorism, through strong statements by Crown Prince Abdallah, Prince Saud Al Faisal, Prince Naef and of religious leaders. The Grand Mufti of the Kingdom and the chairman of the Supreme Court both publicly condemned the 11 September attacks.
- Saudi Arabia has also been the victim of many a terrorist attack, such as the attack against the Great Mosque of Mecca (1979), the bombings Riyadh (1195) and in Al Khobar (1996)
- The government has frozen assets belonging to suspected terrorists. They have announced a review of the fund raising activities of some organisation and the review of money laundering activities.
|
President Bush meets with Saudi Arabia's Foreign Minister Prince Saud al-Faisal in the Oval Office Sept. 20. |
"Combating terrorism is a common global goal for all the countries of the civilized world. Terrorism is against the grain of all religious values and principles especially Islam. It also contradicts the basic human rights of security, peace and international stability." HRH Saud Al-Faisa, Saudi Arabia’s Foreign Minister, 01 Jan 2002 |
Jordan
- It has itself suffered from terrorist attacks and has lost several public figures in this connection, including two Prime Ministers.
- The collection of funds to organisations is controlled by law, and can only be collected after a clear statement of their purpose The government has been consistent with its strong determination in the fight against all kinds of terrorism.
|
|
"September 11th tragedy, I think it's very obvious that those that are on the side of good, those that are on the side of bad, and there's some countries in the middle that haven't made up their minds. So I think that the policy of the United States and the rest of us have been to be very clear to everybody on which side you want to choose. And I think the President has been very articulate from the beginning of the 11th of September that there is a new world, there's a new expectation of how countries are supposed to react. And those countries better make up their minds pretty quickly. And I endorse tremendously that view and that position." King Abdullah 0f Jordan, 01 Feb 2002 |
Kuwait
- Kuwait has given its full support for operation Enduring Freedom
|
|
"…the Government of Kuwait has taken certain steps to ratify the rest of the international treatment, which had been passed by the United Nations. And it is now in front of the parliament. Among other steps which we have taken, that we have put all the charity organisations in Kuwait under complete control of the financial vehicles of Kuwait, like the Central Bank and the Ministry of Finance. We never had such kind of tight control, but now every charity activity will be under tight control of the government." His Excellency Shaykh Sabah al-Ahmad Al Sabah, Acting Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs of the State of Kuwait, 07 Nov 2001 |
|
All around the world counties are uniting by tightening up their legal framework and working together to eradicate international terrorism. There is still work to do, but Coalition countries are committed to the fight. |
|
One of the most important aspects in the War on Terrorism is the fight to stop the financing of terrorist organisations. This fight is difficult, terrorist organisations not only derive funding from general crime but they mask themselves as legitimate businesses and even charities. Coalition countries have demonstrated their resolve to tighten up regulations and block loopholes. |
The Americas
USA
- The U.S. government is taking action to freeze terrorist bank accounts and disrupt fund-raising and recruitment.
- Since Sept 11 U.S. has now "designated" 189 individuals, organisations and financial supporters of terrorism pursuant to Executive Order 13224.
- Since September 11th, $104.8 million has been blocked. $34.2 million in the U.S. and $70.5 million overseas.
- The US has not just acted against the Al Qa’ida network. For example, on February 26, the US acted against ETA, the Basque Terrorist organisation.
|
|
"Our crackdown on terrorists is blind to nationality and origin. Rather, it’s a net that is being cast on all terrorist parasites that threaten our allies and our national security. By taking this action we join many nations to act forcefully against such terrorists." US Treasury Secretary, Paul O’Neill, February 26, 2002 |
Mexico
- Mexico is presently completing the constitutional procedures to become a party to the International Convention for the Suppression of the Financing of Terrorism and is studying the legislative reforms that will be required in order to make the financing of terrorism an autonomous offence.
- It is preparing a series of draft amendments to the Federal Penal Code, the Federal Code of Criminal Procedure and the Federal Organised Crime Act in order to provide the necessary legal means for the effective suppression of this crime.
Europe
Germany
- More than 200 bank accounts containing more than $4 million total have been frozen as part of financial sanctions against terrorist networks.
- The Federal Criminal Police Office has set up an independent unit responsible for the surveillance of suspicious financial flows.
- Among the measures to prevent money laundering are the use of electronic data processing systems to ensure that banks are properly screening their clients and business relationships and the requirement that banks set up internal security systems.
UK
- In the fight against the financing of terrorism and in co-ordination with international partners, the UK has circulated a list of 46 organisations and 16 individuals to financial institutions requiring that assets belonging to them be frozen.
- The Proceeds of Crime Bill was introduced at the House of Commons on 18th October 2001 and contains measures to remove illegally gained assets from criminals, including terrorists.
|
|
"The ready supply of finance is the lifeblood of modern terrorism. Those who finance terrorism are as guilty as those who commit it. UK domestic controls of terrorist financing are already among the best in the world, but we will do whatever is necessary to deprive terrorists of the funds they rely on. Just as there is no safe haven for terrorists there is no safe hiding place for their funds." UK Finance Minister, Gordon Brown, 2 November 2001 |
- Backed by UN Security Council Resolutions 1373 which criminalizes the financing of terrorism and 1390 which orders the freezing of the funds of the Taliban, Osama bin Laden and individuals and entities associated with him:
- over 200 countries and jurisdictions have expressed support for the fight against terrorist financing. Some 150 countries have issued orders to freeze terrorist assets.
- since 11 September over $100 million of terrorist funds has been frozen world-wide
- UK Government has co-operated fully in taking simultaneous freezing action with the US
- UK’s many investigative and law enforcement agencies are actively engaged in the fight against terrorism – in particular by disrupting and cutting off the finances of terrorist organisations
- UK Government has introduced a range of new powers to enable the swift and effective freezing of assets
- Since 11 September, the UK Government has ordered the freezing of assets of over 200 individuals and over 100 organisations
- UK Government is working actively to ensure that the bulk of the $100 million frozen under the Taliban regime is returned to the new, legitimate Government of Afghanistan
- Technical assistance is critical to implementing effective anti-terrorist controls in winning over governments and peoples
Asia
Turkey
- Turkey has comprehensive legislation to combat terrorism and is fully committed to the measures taken in the international fight against terrorism.
- The authorities are working closely with international authorities on measures to freeze assets of terrorist organisations.
China
- In recent years, the central Government of China has promulgated a series of laws and regulations concerning money-laundering.
- In September 2001, the People’s Bank of China set up a special anti-money-laundering task force charged with the unified leadership and deployment of anti-money-laundering operations throughout the Chinese banking system.
- Efforts are also being stepped up to revise regulations governing cash management and to set up a system to report suspicious cash transactions; a centre for overseeing financial transactions and payments to prevent money-laundering is under active development
|
|
"We are determined to fully implement the anti-terrorism measures under the relevant Resolutions of the United Nations Security Council. Hong Kong will spare no effort to prevent and suppress terrorist financing, and will continue to strengthen preventive measures and law enforcement in this regard both domestically and internationally through its Presidency of the Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering." Spokesman for the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, 06 March 02 |
Africa
Kenya
- The authorities have acted to exert greater control on foreign-exchange bureau’s linked to the Al-Barakat organisation, the major remittance company in Somalia.
|
Years of civil war, compounded by the Taliban rule and the worst drought in memory, left Afghanistan impoverished and mired in an extended humanitarian crisis. The Coalition has helped the people of Afghanistan to throw off the shackles of the Taliban and the occupying forces of Al-Qa’ida. Through the International Conference on the Reconstruction of Afghanistan in Tokyo the international community demonstrated its long term commitment to Afghanistan. The Coalition is now helping the people of Afghanistan to rebuild their country. |
USA
- As of February 2002 the US has contributed more than $230m in humanitarian assistance for Afghanistan.
- Even before the events of September 11, Afghanistan was the United States' top recipient of humanitarian aid, providing $174 million in fiscal year 2001.
- The U.S. has pledged nearly $300 million in this fiscal year alone for Afghan relief and reconstruction. The international community, including the U.S., has pledged $1.8 billion in aid this fiscal year, and $4.5 billion in aid over the next five years.
- As of March 1, the World Food Programme (WFP), with the support of the U.S. government, had delivered 333,000 metric tons of food into Afghanistan since October 2001. In December alone, the WFP delivered 116,000 metric tons of food—more food than ever before in one month. Despite this tremendous success, there are still people in remote areas who need help. The U.S. government will continue to provide food assistance.
- The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) provided 240,200 metric tons of wheat in fiscal year 2001 and will provide $45 million in food aid this fiscal year.
- USAID is providing more than $117 million in food assistance to Afghanistan in this fiscal year.
- Between October 7 and December 13, the Department of Defense air-dropped 2,423,700 Humanitarian Daily Rations (HDRs) to Afghans.
- The State Department’s Bureau of Population, Refugees and Migration (PRM) already has contributed $20.4 million to assist victims of conflict inside Afghanistan through the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC).
- USAID has funded airlifts of critical commodities to Afghanistan. The airlifts have provided shelter materials, tents, health supplies and high-energy food items for people at risk in Afghanistan. Ten medical supply shipments provided enough medical supplies and medicine to support 100,000 people for three months.
- Emergency relief supplies delivered into Afghanistan include more than 75,000 blankets, 200 metric tons of high-energy food items and 10,000 cooking sets. In addition, USAID provided mattresses, clothes, stoves, firewood, lanterns and water containers. USAID funding provided 2,756 tons of cooking and heating charcoal to approximately 96,000 of Afghanistan's most vulnerable people. The U.S. is providing emergency shelter and rebuilding damaged homes of thousands of Afghans.
- Through America’s Fund for Afghan Children, America’s boys and girls donated one dollar each to provide food and medical help for the children of Afghanistan. So far, nearly $4.4 million dollars has gone to provide food, shelter, clothing, medicine, and school supplies.
- As part of its Food-for-Education program, the WFP, with USAID support, the US is distributing food to schoolchildren in several districts of Badakhshan Province, in north-eastern Afghanistan. Approximately 27,000 children and 1,500 teachers and service staff in 50 schools have received a four-month ration of wheat flour. A USAID-funded program is encouraging Afghan women and girls to read by hosting reading classes and improving the country's libraries. USAID is funding the training of the library staffs and supplying more books.
- The U.S. is spending over $10 million to improve health care in Afghanistan. Funds are being used to rehabilitate health clinics, provide primary health care, train community health workers and vaccinate children.
Canada
- Canada has provided Afghanistan with $160 million in humanitarian assistance since 1990, $16 million of which was disbursed after September 11, 2001.
- At the Tokyo Conference on Reconstruction in Afghanistan on January 21 and 22, International Co-operation Minister Susan Whelan pledged a further $100 million for humanitarian aid and reconstruction assistance in Afghanistan.
- Canada provides an average of $12 million per year for humanitarian aid to Afghanistan. The funds support the work of several non-governmental organisations, United Nations agencies and the International Committee of the Red Cross.
|
|
"Canada is part of an unprecedented coalition of nations that has come together to fight the threat of terrorism...I have made it clear from the very beginning that Canada would be part of this coalition every step of the way...all Canadians understand what is being asked of the men and women of our Armed Forces and their families." Canadian Prime Minister, Jean Chretien, 8 Oct 2001 |
UK
- The UK is presently the lead nation in the International Security Assistance Force. It presently has more than 1700 troop deployed with ISAF.
- Between 1997 and September 2001, the UK Department for International Development (DFID) provided over £32 million to the people of Afghanistan for emergency food, shelter, healthcare and water supplies, as well as support for agriculture, mines clearance, education, monitoring and advocacy in relation to human rights, and co-ordination.
- Assistance was channelled through a range of UN agencies, the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) and non-governmental organisations (NGOs).
|
|
"Terrorist groups, criminals, drug dealers and disorderly forces who want to be destructive and spread hate and violence in the world are nurtured by, and hide themselves in, failed states. We always need the capacity to prevent such action and to build efficient modern states that are part of the international community so that it is not vulnerable to terrorist organisations such as those responsible for 11 September." Clare Short, UK International Development Secretary,
|
- Since September 11th DFID has contributed £60 million for UK humanitarian assistance. Funds have been allocated to UN agencies (almost £37 million), the Red Cross movement (£5 million) and various NGOs.
- Of this money over £4 million has been channelled into Quick Impact Projects (QIPs) since January 2002. QIPs are designed, as a contribution to the wider international effort, to quickly demonstrate the substantial peace dividend in seeing the Interim Authority as a positive development for the future peace and stability of the country.
- Allocations have been made to agencies as follows:
- £6 million to the International Organisation for Migration (IOM) for projects in Afghanistan, and to identify Afghan professionals to assist recovery;
- £5 million to the Red Cross Movement: £3 million to ICRC and £2 million to the IFRC for protection and relief activities;
- Approximately £12 million to the NGOs for immediate humanitarian and recovery assistance to vulnerable Afghans inside Afghanistan or who have become refugees
- £5 million for quick impact recovery projects; and £2.2 million for direct operations by DFID in support of international humanitarian agencies.
- Allocations to UN agencies include technical personnel, logistical and other material support. This includes: expert personnel for Mr Brahimi’s office; a site planning specialist to UNHCR; two specialists to OCHA to set up a Humanitarian Information Centre; four air operations advisers to UNHCR and WFP; and a nutrition specialist to UNICEF.
- A DFID Field Support Team was deployed to assist the UN in re-establishing its office in Mazar-e-Sharif. DFID has also opened an office in Kabul, in addition to its long-established regional hub in Islamabad and temporary staff deployments to other countries neighbouring Afghanistan.
- At the Tokyo conference, the UK announced a further pledge of £200 million assistance to Afghanistan over the next 5 financial years.
Germany
- At the request of the interim authority in Kabul the German Government is assisting in the rebuilding of the Afghan police forces by providing training and equipment. It presently has more than 330 troop deployed with ISAF
- In January 2002 Germany became the first foreign nation to have its ambassador fully accredited by the interim administration in Kabul.
- Germany has underscored its commitment to averting humanitarian disaster and to securing lasting political stability in the region, most recently with a pledge of $278 million in aid over the next four years for the reconstruction of Afghanistan
- In Tokyo, Germany pledged $69.4 million in 2002 and a total of $278 million for reconstruction efforts over the next four years. The combined European Union contribution of $550 million makes up more than 30% of the total pledged by all nations at the Tokyo conference to assist Afghanistan in 2002.
- Germany was one of the first nations to contribute to the Afghanistan Interim Authority Fund, a trust fund within the UN framework set up to support the work of the Interim Government, with a contribution of $1.7 million in early January 2002.
- Germany provided $46.2 million in humanitarian aid and development-oriented assistance to Afghanistan in 2001, the same year it held the chairmanship of the Afghanistan Support Group, a co-ordination mechanism for humanitarian donors.
- Germany served as host of the UN Talks on Afghanistan on the Petersberg, which concluded on December 5, 2001, and produced the -Bonn Agreement,- a blueprint for the political stabilisation of Afghanistan over the next three years
Italy
- As of February 2002 Italy has contributed more than $33m in humanitarian assistance for Afghanistan.
- It presently has more than 350 troops deployed with ISAF.
Finland
- Finland participated in the donors pledging conference in Tokyo and made a three year pledge of 10 million euros annually. The 2002 contributions will be divided evenly between humanitarian assistance and reconstruction.
- Finland is planning to send a contingent of about 50 troops, consisting of a special civilian and military co-operation (CIMIC) unit as well as liaison officers.
- As mandated by the UN, the operation aims at keeping peace in the capital, Kabul, and surrounding areas in order to facilitate a safe and secure environment for the interim government of Afghanistan and the assisting UN personnel.
- It is envisaged that the Finnish troops will be involved in the co-ordination of humanitarian assistance and liase with the interim government and various military operators.
Netherlands
- The Dutch humanitarian aid is directed to the people of Afghanistan and the Afghan refugees in neighboring countries.
- In addition to its annual contribution of $ 8 m in humanitarian aid, the Netherlands has pledged almost $ 100 m for humanitarian aid and reconstruction:
- $ 27.5 m (UN donor alert 2001)
- $ 5 m (International Red Cross)
- $ 3 m (Trustfund UNDP)
- $ 1 m (UNIFEM)
- $ 62 m (Tokyo Conference)
- The Netherlands is also contributing to the humanitarian aid provided by the European Union, which has a total value of $ 329 million.
- Around 220 Dutch troops participate in the German-Dutch-Austrian-Danish infantry battalion deployed in Kabul in the framework of ISAF. These troops will stay in Afghanistan for a period of six months.
Sweden
- Humanitarian and reconstruction assistance amounting to $100 million, for the period 2002-2004.
- In Tokyo they pledged over $13m.
Japan
- Japan was a co-Chair and hosted the conference to help reconstruct Afghanistan. As of February 2002 Japan has contributed more than US$90m in humanitarian assistance for Afghanistan.
Jordan and Saudi Arabia
- Jordanian troops have set up a hospital at Mazar-e-Sharif.
- In the Tokyo conference Saudi Arabia pledged more than $12m to Afghanistan
Afghanistan
|
|
|
"Afghanistan could have not been freed from the occupation of terrorism, from the presence of terrorism, without the help of the friends that we have, without the presence of your troops there, without the sacrifice that they made and without the contribution that you made to Afghanistan's liberation." Hamid Karzai, Chairman of the Interim Administration of Afghanistan,
|
7. Protecting the Future
|
"Combating terrorism is a common global goal for all the countries of the civilised world. Terrorism is against the grain of all religious values and principles especially Islam. It also contradicts the basic human rights of security, peace and international stability" HRH Saud Al-Faisal, Foreign Minister of Saudi Arabia, 10 Oct 2001 |
|
|
"Our war on terror is well begun, but it is only begun. This campaign may not be finished on our watch -- yet it must be and it will be waged on our watch." President Bush, State of the Union address, 29 Jan 2002 |
|
Coalition countries are co-operating closely to forestall future attacks from international terrorism There are many countries where adoption of terrorist methods or the presence of terrorist or extremist networks causes us grave concern. We will take the action we deem necessary in support of this aim, including military action, if absolutely necessary. They are also countries working to constrain those groups and regimes believed to be seeking to acquire weapons of mass destruction. The War has just begun, there will be many tough fights ahead, but the coalition remains steadfast in its objectives to defeat international terrorism and protect the lives of its people. |